Performance
Performance
RuleGo does most of its work in the initialization phase. Executing the rule chain hardly has any performance loss. In addition, RuleGo uses a directed acyclic graph to represent the rule chain, and each input message only needs to be processed along the path in the graph, without matching all the rules, This greatly improves the efficiency and speed of message processing, and also saves resources and time. The routing algorithm can achieve: no matter how many nodes the rule chain has, it will not affect the node routing performance.
However, RuleGo itself has good performance, but what determines the overall performance of the rule chain is the business logic of the nodes. If your components have a lot of database queries or remote calls, the throughput will not be very high.
Performance suggestions:
- Optimize the performance of the remote call interface service.
- Use the built-in AOP to implement data caching after node processing, reducing node repetition.
- Replace the built-in JSON encoding and decoding, use a higher performance JSON library.
- Use custom components to implement higher performance components that meet the special needs of the project.
- RuleGo can support a large number of concurrent requests on a single ordinary machine. You can also deploy multiple RuleGo instances, add a load balancer, and distribute the requests to different RuleGo instances for processing, achieving massive data processing.
# Performance test case
The following are the performance test results of the /examples/server /api/v1/msg/{chainId}/{msgType} interface.
Processing rule chain: js filter->js transform node.
Machine configuration CPU & memory: 2 cores (vCPU) & 2GiB
Bytes per request: 142 bytes
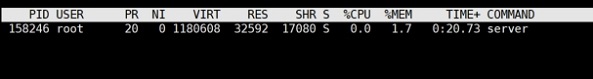
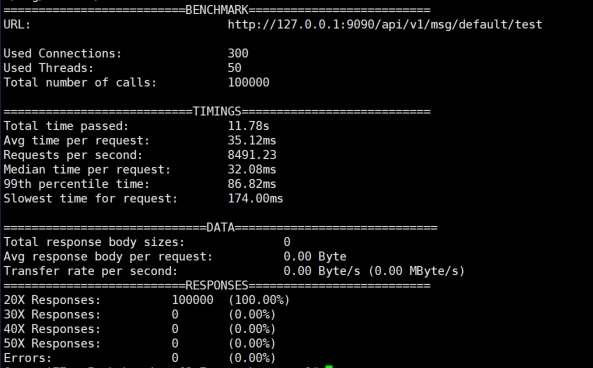
- 300 concurrent test results
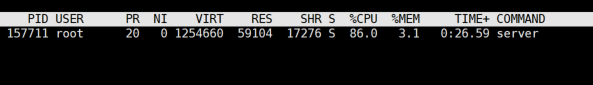
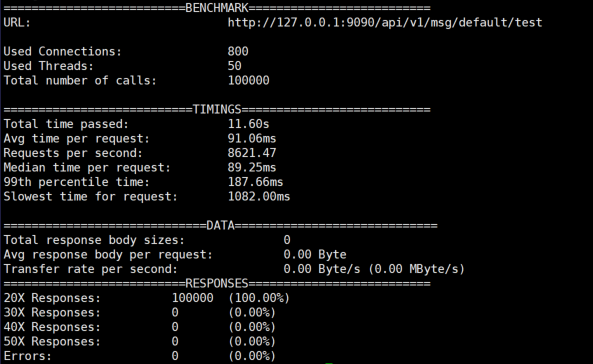
- 800 concurrent test results
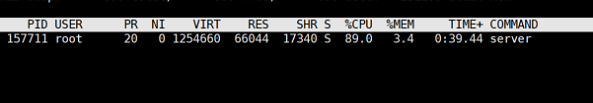
- CPU and memory usage of RuleGo at startup and idle