 Config
Config
# title: Config article: false author: name: rulego link: https://github.com/rulego/rulego (opens new window) date: 2023-09-13 21:24:41 permalink: /pages/d59341/
The Config (opens new window) of the rule engine instance is a global configuration. You can modify the config as follows:
config := rulego.NewConfig()
ruleEngine, err := rulego.New("rule01", []byte(ruleChainFile), rulego.WithConfig(config))
2
# OnDebug
Type: func(flowType string, nodeId string, msg RuleMsg, relationType string, err error)
- flowType: IN/OUT, representing the event type of flowing into (IN) or out of (OUT) the component.
- nodeId: Node ID.
- msg: Message structure, where the message ID is unique.
- relationType: If flowType=IN, it represents the connection relationship between the previous node and this node (e.g., True/False); if flowType=OUT, it represents the connection relationship between this node and the next node (e.g., True/False).
- err: Error information.
Global callback function for node debugging information. When the debugMode=true is set in the rule chain node configuration, both the In and Out processes of the node will trigger this callback. You can use this callback function to log each node's execution details, such as execution time, input messages, and output messages. It supports dynamically enabling or disabling the debugMode field for nodes.
TIP
The custom logic in the OnDebug callback function is triggered asynchronously and cannot guarantee the order of execution.
Visualization reference:
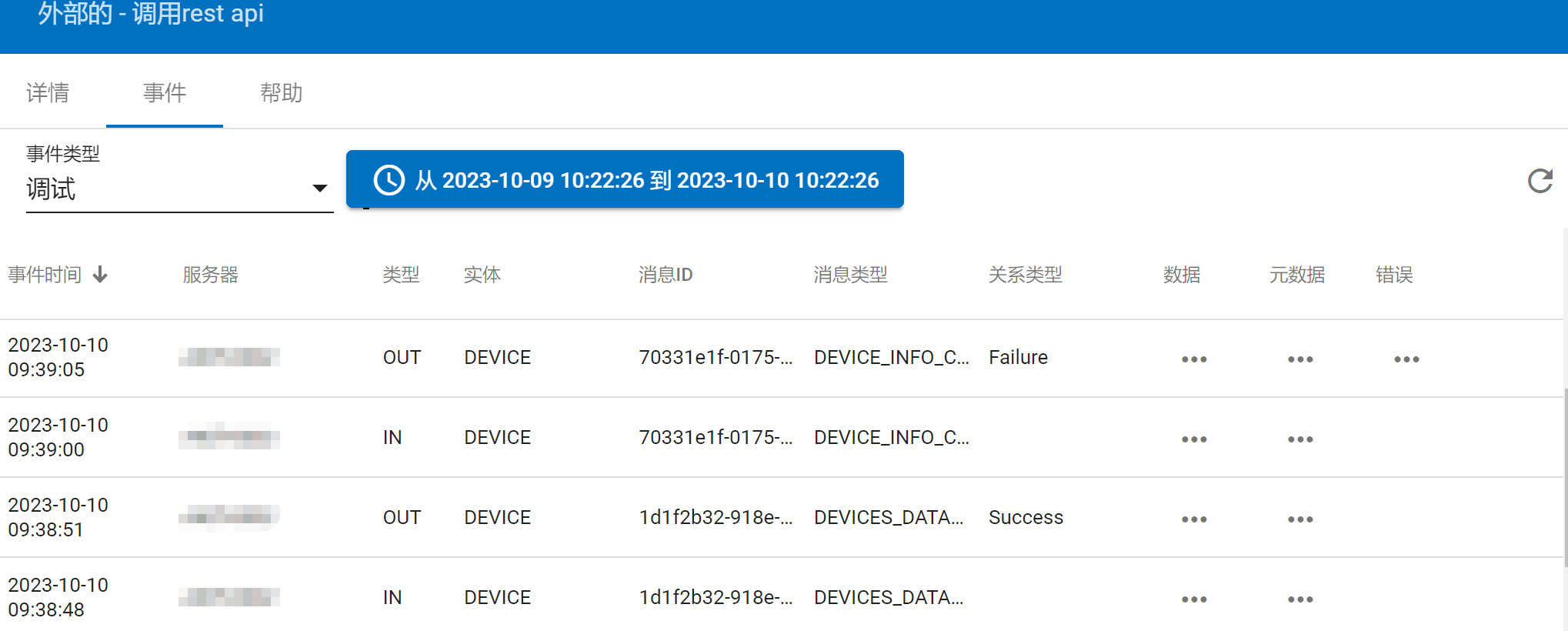
# OnEnd (Deprecated)
Deprecated, use types.WithOnEnd instead.
Type: func(msg RuleMsg, err error)
- msg: The message after processing by the end node.
- err: Error information.
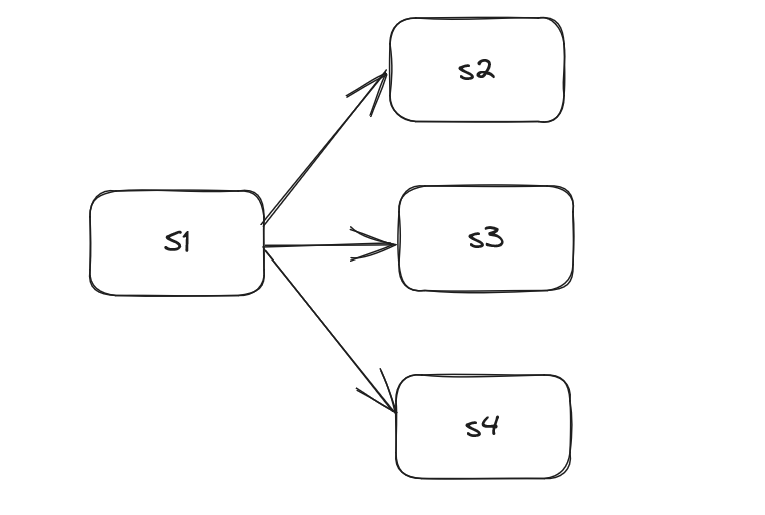
Global callback function for rule chain execution completion. If a rule chain has multiple endpoints, this function will be called multiple times. For example, if s1 triggers s2, s3, and s4 simultaneously, the onEnd event will be triggered three times, with msg being the execution results of s2, s3, and s4 respectively. The rule chain is shown in the following figure:
TIP
The OnEnd function configured in the config is global for the rule engine instance. You can also configure an end callback function for each message using the following method:
ruleEngine.OnMsg(msg, types.WithOnEnd(func(ctx types.RuleContext, msg types.RuleMsg, err error) {
// End callback function
}))
2
3
If you want to execute a callback function once after the rule chain processing is complete, you can use the following method:
ruleEngine.OnMsg(msg, types.WithOnAllNodeCompleted(func() {
// Processing completed
}))
2
3
# OnEndWithFailure
Type: bool
Default: true
Indicates whether to trigger the OnEnd callback when no connected node is found and the relation type is Failure.
# ScriptMaxExecutionTime
Type: time.Duration
The default timeout for JavaScript script execution is 2000 milliseconds.
# Pool
Type: types.Pool
The goroutine pool interface. If not configured, it defaults to using go func.
By default, the built-in pool.WorkerPool is used. It is compatible with the ants goroutine pool. You can use the ants implementation by importing the corresponding library. For example:
pool, _ := ants.NewPool(math.MaxInt32)
config := rulego.NewConfig(types.WithPool(pool))
2
TIP
The built-in pool.WorkerPool is inspired by FastHttp and has higher performance and lower memory usage compared to ants.
# ComponentsRegistry
Type: types.ComponentRegistry
The component library registry. By default, it uses rulego.Registry.
# Parser
Type: types.Parser
The rule chain parsing interface. By default, it uses rulego.JsonParser, but you can implement a custom rule chain DSL.
# Logger
Type: types.Logger
The logging interface. By default, it uses DefaultLogger(). The log component uses this logger.
# Properties
Type: types.Metadata
Global properties in key-value format.
Rule chain node configurations can replace variable content using the ${global.propertyKey} syntax.
global.is a built-in variable that retrieves content fromconfig.Propertiesfor replacement (the replacement logic is executed only once during node initialization). For an example, refer to node_config (opens new window).- Additionally, script engines like JavaScript and Lua can access global property values using
global.propertyKey.
Example in Lua script:
-- Calling a global configuration parameter
-- Corresponding to JS: var value=global.propertyKey;
local propertyValue = global.propertyKey
2
3
# UDF
Type: map[string]interface{}
Register custom Golang functions and native scripts, allowing script engines such as JavaScript/Lua to call them directly. Two registration methods are supported:
# 1. Golang Function Registration
Two registration methods are supported:
# 1.1 Direct Function Registration
config := rulego.NewConfig()
// Method 1: Using types.Script for wrapping
config.RegisterUdf("add", types.Script{
Type: types.All, // callable by both Lua and JS scripts
Content: func(a, b int) int {
return a + b
},
})
// Method 2: Direct function registration, callable by both Lua and JS scripts
config.RegisterUdf("handleMsg", func(msg map[string]interface{}, metadata map[string]string, msgType string) string {
msg["processed"] = true
return "processed_" + msgType
})
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
# 1.2 Struct Method Registration
// Define a utility struct
type ToolTest struct {
}
// Example of a struct method: Query
func (t *ToolTest) Query(id string) string {
return "result:" + id
}
// Example of a struct method: Delete
func (t *ToolTest) Delete(id string) bool {
return true
}
// Register all exported methods of the struct pointer
var tool = &ToolTest{}
config.RegisterUdf(
"tool", // Registration name
tool, // Struct pointer
)
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
# 2. Native Script Registration (JS)
Supports directly injecting JavaScript source code into the script context.
// Register JavaScript utility functions
config.RegisterUdf("utils", types.Script{
Type: types.Js,
Content: `var utilsFunc={
dateFormat:function(date,fmt){
// Date formatting logic
return fmt;
},
isArray:function(arg){
if (typeof Array.isArray === 'undefined') {
return Object.prototype.toString.call(arg) === '[object Array]'
}
return Array.isArray(arg)
},
isObject: function(value){
if (!data || this.isArray(data)) {
return false;
}
return data instanceof Object;
},
isNumber: function(value){
return typeof value === "number";
},
}
`,
})
// Usage: let result = utilsFunc.dateFormat(new Date(), 'YYYY-MM-DD')
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
# 3. Native Script Registration (Lua)
Supports directly injecting Lua source code into the script context.
config.RegisterUdf("myFuncDirect", types.Script{
Type: types.Lua,
Content: "function(a, b) return a + b end", // UDF is a function definition string
})
// Usage: local result = myFuncDirect(5, 6)
2
3
4
5
# 4. Registering Lua-Specific Functions
// Register a Lua custom function, callable only by Lua scripts
config.RegisterUdf("add", types.Script{Type: types.Lua, Content: func(L *lua.LState) int {
a := L.CheckNumber(1)
b := L.CheckNumber(2)
L.Push(lua.LNumber(a + b))
return 1
}})
2
3
4
5
6
7
# JavaScript Call Example
// Call the add function registered by Go
let sum = add(10, 20);
// Call the registered utils utility function
let formattedDate = utilsFunc.dateFormat(new Date(), 'YYYY-MM-DD');
let isArray = utilsFunc.isArray([1,2,3]);
// Example of calling a struct method
let queryResult = tool.Query('1001');
let deleteStatus = tool.Delete('1001');
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
# Lua Call Example
-- Call the add function registered by Go
local result = add(10, 20)
2
# Aspects
Type: []Aspect
AOP aspect list. Example:
// Adding a component fault tolerance aspect
config := rulego.NewConfig(
types.WithAspects(&aspect.SkipFallbackAspect{ErrorCountLimit: 3, LimitDuration: time.Second * 10})
)
2
3
4
# NodeClientInitNow
Type: bool
Whether network client components (e.g., MQTT client components, Kafka client components, etc.) should be initialized immediately during initialization. Default is false, meaning they are initialized on the first call.
true: Initialize immediately during initialization. If initialization fails, the rule chain will not start.false: Initialize on the first call. If initialization fails, the rule chain will start, but the component call will fail.
# AllowCycle
Type: bool
Whether to allow circular dependencies between nodes in a rule chain. Default is false, meaning circular dependencies are not allowed.
# Cache
Type: types.Cache
The cache is used for data sharing between different rule chains or between different execution contexts of the same rule chain instance. It has two levels: chain and global.
- chain: Cache at the current rule chain level, operating within the current rule chain namespace. It is used for data sharing between different execution contexts within the same rule chain instance. If the rule chain instance is destroyed, all caches under this rule chain namespace will be automatically deleted.
- global: Cache at the global level, operating within the global namespace. It is used for data sharing across different rule chains.
The framework provides operations for both levels of cache within the same cache instance. The following are ways to operate the cache:
# Operating Cache in JavaScript Scripts
In JavaScript script-related components, such as JavaScript Script Transformer and JavaScript Script Filter, you can obtain the cache object through the built-in variable $ctx and call the corresponding methods to operate the cache.
let cache = $ctx.ChainCache(); // Get the cache for the current rule chain level, operating within the current rule chain namespace
// let cache = $ctx.GlobalCache(); // Get the global-level cache, operating within the global namespace
let err = cache.Set("key", "value"); // Set a cache item that never expires
let err = cache.Set("key2", "value2", "10m"); // Set a cache item that expires after 10 minutes
// Setting a complex structure
var user1 = {"name": "John", "age": 30};
$ctx.ChainCache().Set("user1", user1);
let value = cache.Get("key1"); // Get a cache item
let ok = cache.Has("key1"); // Check if a cache item exists
let err = cache.Delete("key1"); // Delete a cache item
let values = cache.GetByPrefix("prefix_key"); // Get all cache items with a specified prefix
let err = cache.DeleteByPrefix("prefix_key"); // Delete all cache items with a specified prefix
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
# Operating Cache in Lua Scripts
In Lua script-related components, such as Lua Script Transformer and Lua Script Filter, you can obtain the cache object through the built-in variables ChainCache or GlobalCache and call the corresponding methods to operate the cache.
local cache = ChainCache -- Get the cache for the current rule chain level, operating within the current rule chain namespace
-- local cache = GlobalCache -- Get the global-level cache, operating within the global namespace
cache.Set('key1', 'value1') -- Set a cache item that never expires
cache.Set('key2', 'value2', '10m') -- Set a cache item that expires after 10 minutes
local value = cache.Get('key1') -- Get a cache item
local ok = cache.Has('key1') -- Check if a cache item exists
cache.Delete('key1') -- Delete a cache item
local values = cache.GetByPrefix('prefix_key') -- Get all cache items with a specified prefix
cache.DeleteByPrefix('prefix_key') -- Delete all cache items with a specified prefix
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
# Operating Cache in RuleContext
During the OnMsg lifecycle of the rule engine component, you can obtain the cache object through the RuleContext object and call the corresponding methods to operate the cache.
cache := ctx.ChainCache() // Get the cache for the current rule chain level, operating within the current rule chain namespace
// cache := ctx.GlobalCache() // Get the global-level cache, operating within the global namespace
err := cache.Set("key1", "value1", "0") // Set a cache item that never expires
err := cache.Set("key2", "value2", "10m") // Set a cache item that expires after 10 minutes
v := cache.Get("key1") // Get a cache item
ok := cache.Has("key1") // Check if a cache item exists
err := cache.Delete("key1") // Delete a cache item
values := cache.GetByPrefix("prefix_key") // Get all cache items with a specified prefix
err := cache.DeleteByPrefix("prefix_key") // Delete all cache items with a specified prefix
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
# Operating Cache in Components
You can also operate the cache through components. For more information, refer to Cache Get Component, Cache Delete Component, and Cache Set Component.
# Cache Implementation Configuration
By default, RuleGo uses the built-in local memory cache (utils/cache.MemoryCache) and provides a global default instance cache.DefaultCache (with a default GC cleanup cycle of 5 minutes). If you do not specify a custom cache implementation using the types.WithCache option, the system will automatically use this default memory cache.
If you need to use other cache types (e.g., Redis, Memcached), you need to implement the types.Cache interface and inject it using the types.WithCache option when creating the Config.
The types.Cache interface is defined as follows:
package types
// Cache defines the interface for cache storage
// It provides key-value storage and retrieval capabilities, supporting expiration times
// Implementations must ensure thread safety
type Cache interface {
// Set stores a key-value pair in the cache, optionally with an expiration time
// Parameters:
// - key: The cache key (string)
// - value: The value to be stored (interface{})
// - ttl: The time-to-live string (e.g., "10m", "1h")
// Returns:
// - error: If the ttl format is invalid, an error is returned
// Note: If ttl is 0 or an empty string, the item will never expire
Set(key string, value interface{}, ttl string) error
// Get retrieves a value from the cache by key
// Parameters:
// - key: The cache key to look up (string)
// Returns:
// - interface{}: The stored value, or nil if it does not exist or has expired
Get(key string) interface{}
// Has checks if a key exists in the cache
// Parameters:
// - key: The cache key to check (string)
// Returns:
// - bool: True if the key exists and has not expired, otherwise false
Has(key string) bool
// Delete deletes a cache item by key
// Parameters:
// - key: The cache key to delete (string)
// Returns:
// - error: The current implementation always returns nil
Delete(key string) error
// DeleteByPrefix deletes all cache items with the specified prefix
// Parameters:
// - prefix: The key prefix to match (string)
// Returns:
// - error: The current implementation always returns nil
DeleteByPrefix(prefix string) error
// GetByPrefix retrieves all values whose keys match the specified prefix
// Parameters:
// - prefix: The key prefix to match (string)
// Returns:
// - map[string]interface{}: A map of matching key-value pairs
GetByPrefix(prefix string) map[string]interface{}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
Configuration example:
// Using a custom cache implementation
config := rulego.NewConfig(types.WithCache(&myCacheImpl{}))
// If using the default in-memory implementation, no explicit configuration is needed; RuleGo will automatically use cache.DefaultCache
// config := rulego.NewConfig()
2
3
4
5
